Table Of Content
The main methods of data collection for exploratory research are survey research, qualitative research, literature reviews, case studies, and focus groups. The selection of a specific research design method should align with the research objectives, the type of data needed, available resources, ethical considerations, and the overall research approach. Researchers often choose methods that best suit the nature of their study and research questions to ensure that they collect relevant and valid data.
Qualitative data analysis
Justify choices by linking them to research objectives, addressing reliability and validity. Case study research design is used to investigate a single case or a small number of cases in depth. It involves collecting data through various methods, such as interviews, observations, and document analysis.
Types of research data
Navigating the world of research can be daunting, especially if you’re a first-time researcher. One concept you’re bound to run into fairly early in your research journey is that of “research design”. Here, we’ll guide you through the basics using practical examples, so that you can approach your research with confidence. The research methods you use depend on the type of data you need to answer your research question. Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research.
Complex Innovative Trial Design Meeting Program - FDA.gov
Complex Innovative Trial Design Meeting Program.
Posted: Thu, 11 Apr 2024 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Grounded Theory
A population can be made up of anything you want to study – plants, animals, organisations, texts, countries, etc. In research, a population is the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about, while a sample is the smaller group of individuals you’ll actually collect data from. Experiments are the strongest way to test cause-and-effect relationships without the risk of other variables influencing the results.
The more precisely you define your population, the easier it will be to gather a representative sample. As well as scientific considerations, you need to think practically when designing your research. If your research involves people or animals, you also need to consider research ethics. The first choice you need to make is whether you’ll take a qualitative or quantitative approach.
This has the strength of remaining open-minded about the possible outcomes of the study, and not being restricted to only studying a specifically noted hypothesis from the beginning. This goes against most research designs, where a researcher starts with a hypothesis and then they create a study to test the hypothesis. This sort of study is often valuable in detecting correlations between variables over the course of an intervention. Meta-analyses are considered some of the most valuable and respected research designs because they can demonstrate that there is sufficient data from the scientific community for an authoritative scientific account of a phenomenon or topic. This approach allows the researcher to take the benefits of both methods, using one method to enhance or inform the other. In this sense, it’s extremely practical, designed to achieve tangible results for a specific practitioner in a specific setting.
The function of a research design is to ensure that the evidence obtained enables you to effectively address the research problem as unambiguously as possible. In social sciences research, obtaining evidence relevant to the research problem generally entails specifying the type of evidence needed to test a theory, to evaluate a program, or to accurately describe a phenomenon. However, researchers can often begin their investigations far too early, before they have thought critically about about what information is required to answer the study's research questions. Without attending to these design issues beforehand, the conclusions drawn risk being weak and unconvincing and, consequently, will fail to adequate address the overall research problem. Qualitative research aims to understand and describe behaviour by exploring beliefs, motivations or reasoning. So qualitative research focuses on life experiences; they are more about the “why” and “how”.
When space is at a premium—and a quiet spot to conduct business is the end goal—it's time to put every unused corner to use. Designer Corey Damen Jenkins proved just how versatile a few extra square feet could be in this Michigan home, where he transformed a lofted space above the foyer into a focus zone worthy of a CEO or 4.0 brainiac. Several studies also have shown that asking a more specific question before a more general question (e.g., asking about happiness with one’s marriage before asking about one’s overall happiness) can result in a contrast effect. Although some exceptions have been found, people tend to avoid redundancy by excluding the more specific question from the general rating. A content analysis will involve systematic and objective coding and interpreting of text or media to identify patterns, biases , themes, ideologies, and so on (Schweigert, 2021). Content analysis has a range of sub-designs, such as semiotic analysis, multimodal analysis, and discourse analysis.
Find Focus
Research design is the blueprint or the framework for conducting a study that outlines the methods, procedures, techniques, and tools for data collection and analysis. Longitudinal research design is used to study changes in a particular phenomenon over time. It involves collecting data at multiple time points and analyzing the changes that occur. The aim of longitudinal research is to provide insights into the development, growth, or decline of a particular phenomenon over time.
They could distribute a survey (quantitative method) to measure levels of motivation, and then conduct interviews (qualitative method) to gain a deeper understanding of factors influencing student motivation. Systematic Review ExampleA health researcher interested in the impact of a plant-based diet on heart disease might conduct a systematic review of all published studies on the topic. They would gather, analyze, and synthesize data from these studies to draw a comprehensive understanding of the current evidence base on this issue. The goal is to gain insights into a group’s practices, behaviors, and culture by observing and interacting with them in their natural environment. This method can provide rich, contextual data but is also time-intensive and requires significant planning to ensure representative sampling and accurate recording of data.
Psychological research indicates that people have a hard time keeping more than this number of choices in mind at one time. When the question is asking about an objective fact and/or demographics, such as the religious affiliation of the respondent, more categories can be used. For example, Pew Research Center’s standard religion questions include more than 12 different categories, beginning with the most common affiliations (Protestant and Catholic).
Cost-Benefit Analysis - A method of comparing the cost of a program with its expected benefits in dollars (or other currency). The benefit-to-cost ratio is a measure of total return expected per unit of money spent. This analysis generally excludes consideration of factors that are not measured ultimately in economic terms. Cost effectiveness compares alternative ways to achieve a specific set of results. Broadly, research design types can be divided into qualitative and quantitative research.
Participants are typically assigned to groups at random in order to control for any extraneous variables that could influence the results. Furthermore, the study may occur in a controlled environment where extraneous variables can be controlled and minimized, allowing for the analysis of cause-and-effect. An experimental research design tends to split research participants into two groups, known as the control group and experimental group(Abbott & McKinney, 2013). The control group receives nothing, or, a placebo (e.g. sugar pill), while the experimental group is provided the dependant variable (e.g. a new medication).
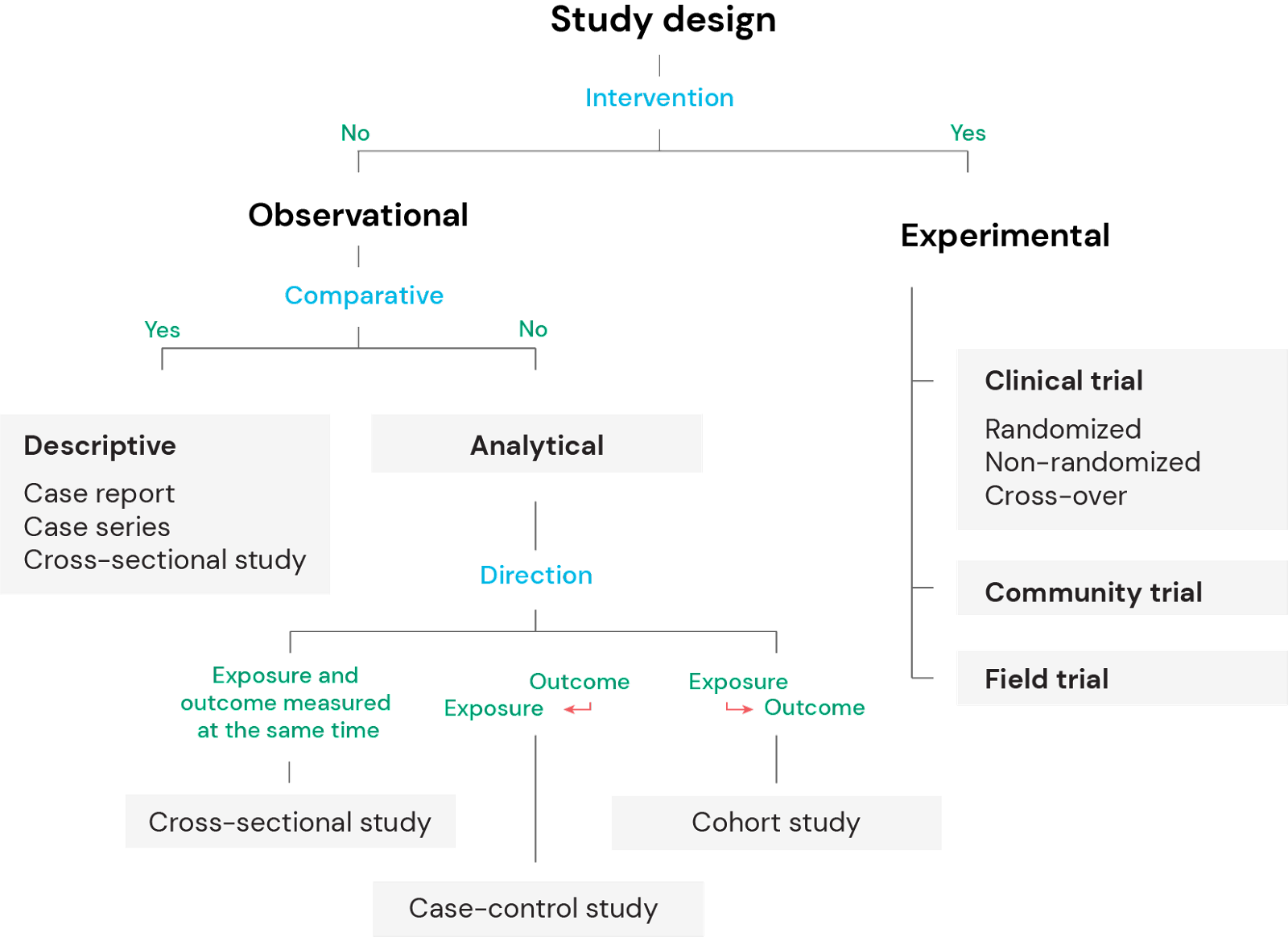
The research design is an important component of a research proposal because it plans the project’s execution. You can share it with the supervisor, who would evaluate the feasibility and capacity of the results and conclusion. Observational studies can be either descriptive (nonanalytical) or analytical (inferential) – this is discussed later in this article. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.
Quantitative research aims to develop objective theories by generating quantifiable numerical data. Random Allocation - A process involving chance used in therapeutic trials or other research endeavor for allocating experimental subjects, human or animal, between treatment and control groups, or among treatment groups. Qualitative Studies - Research that derives data from observation, interviews, or verbal interactions and focuses on the meanings and interpretations of the participants. Lost to Follow-Up - Study subjects in cohort studies whose outcomes are unknown e.g., because they could not or did not wish to attend follow-up visits.
Combines elements of surveys and experiments, allowing researchers to manipulate variables within a survey context. A qualitative research method that aims to develop theories or explanations grounded in the data collected during the research process. Researchers analyze textual, visual, or audio data to identify patterns, themes, and trends. Traverse the realm of correlations with Correlational Studies, scrutinizing interrelationships between variables without inferring causality. Capture snapshots of reality with Cross-Sectional Studies, unraveling intricate relationships and disparities between variables in a single moment. Embark on longitudinal journeys with Longitudinal Studies, tracking evolving trends and patterns over time.